Life Extension Magazine®
Mention erectile dysfunction and most people think of Viagra® and similar drugs.
These drugs temporarily solve “sexual” problems for about half of men.1
Aging men that visit their doctors to get erectile dysfunction drugs often have no idea what causes this condition.
Erectile dysfunction is an early symptom of artery disease. It can show up as a warning sign up to three years before a heart attack or stroke.2
Compelling research demonstrates that certain nutrients boost levels of nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels and enables efficient blood flow—the key to both overall vascular health and male sexual function.3-5
A study published in the March 2017 issue of Andrology found that a significant proportion of erectile dysfunction patients have low levels of L-arginine (a nitric oxide precursor).6 Another recent study shows that supplementing with L-arginine and pine-bark extract significantly boosts erectile function.7
Fortunately, large doses of arginine are no longer needed. That’s because a nitric oxide-boosting equivalent can be obtained with a lower dose of the amino acid chelate, L-arginine aspartate.
These compounds have been shown in previous clinical trials to improve not only erectile dysfunction5,7,8 but also the underlying cardio-vascular cofactors.5,9
Vascular Disease Results In Erectile Dysfunction
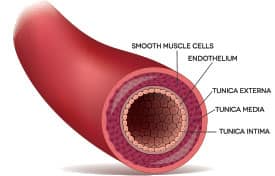
Male sexual dysfunction frequently results from underlying health issues, including prostatic disease, neurological damage, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, multiple sclerosis, medication side effects—and especially, vascular occlusion.10-14
In a study released online in April 2017 by the American Journal of Hypertension, 1,136 men (ages 45 to 84) were scored according to cardiovascular risk factors. A decade later, 58% of the men with the highest cardiovascular disease risk had erectile dysfunction, compared with just 33% of men with the lowest cardiovascular risk.14
Blood flow through the arteries and endothelial function (function of the inner arterial lining) are essential to sexual arousal.2
That’s why erectile dysfunction should trigger an investigation for early indications of cardiovascular disease, such as comprehensive blood tests. But this is almost never the case.
First, many people don’t bother to see a doctor about sexual dysfunction.15
Second, those who do are generally prescribed drugs without regard for underlying cofactors.
Pharmaceutical firms have persuaded the public and medical establishment that sexual symptoms are drug-treatable “diseases” instead of early-warning signs, so mainstream doctors seldom think to investigate further.
The fact is that erectile dysfunction, reduced libido, and loss of fertility are potential predictors of cardiovascular disease, which strikes epidemic numbers of aging individuals.2,16,17
Unaware of these links, many men experiencing sexual difficulties seek prescriptions such as Viagra®, Cialis®, or Levitra®, that work by relaxing the smooth muscles lining the arteries, in turn increasing blood flow into the arteries that supply the penis.
These drugs provide only temporary effects, work for only about half of erectile dysfunction patients, cost as much as $50 a pill without insurance,18 and are associated with side effects ranging from indigestion, flushing, visual disturbances, hearing loss, and headache. Rare but more serious problems include neurologic disorders and heart attack.19-27
More critically, these drugs do not adequately treat an underlying cause of erectile dysfunction—chronic endothelial dysfunction.
Healthy endothelial cells release nitric oxide synthase, an enzyme that catalyzes production of nitric oxide from the amino acid L-arginine.
Nitric oxide triggers relaxation of the smooth muscle in the arteries of the penis, providing the adequate blood flow necessary for an erection. However, dysfunctional endothelial cells, disabled by plaque buildup, can no longer produce sufficient levels of nitric oxide synthase.28
Thankfully, innovative scientists have identified three natural ingredients that boost endothelial function—simultaneously enhancing sexual capability and protecting against heart attack and stroke.
What You Need to Know
 |
Reversing Erectile Dysfunction via Vascular Support
- Painted by pharmaceutical firms as merely a “sexual problem,” erectile dysfunction is generally treated with costly drugs, such as Viagra®, that for some may temporarily alleviate these common symptoms of underlying vascular problems.
- Unfortunately, many aging men—and some doctors—are unaware that this condition is an early-warning symptom, appearing up to three years before a heart attack or stroke.
- An array of persuasive studies show that L-arginine—found in reduced levels in many erectile dysfunction patients—as well as French maritime pine-bark extract and the flavonoid icariin safely boost levels of nitric oxide, the blood flow-promoting key to both healthy male sexual function and overall vascular health.
- Research has shown that these three natural compounds improve both erectile dysfunction and underlying cardiovascular cofactors.
Restore Endothelial Health—and Sexual Potency
Scientists have studied three compounds that modulate the mechanisms underlying erectile dysfunction.
French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine aspartate—an amino acid chelate—work together to stimulate nitric oxide synthase, thus producing sufficient bioactive nitric oxide to induce and maintain an erection.5
Icariin—a flavonoid compound used in Chinese herbal medicine—further supports the ability to maintain an erection by blocking phosphodiesterase-5, the enzyme responsible for causing erections to subside.29 This enzyme-blocking effect mimics the primary mechanism of Viagra®, which delivers no other benefit.
Compelling human trials demonstrate that this nutrient blend improves male sexual function and underlying vascular health through an array of health effects, delivering:
- Normal erectile function5,8,9
- Enhanced sperm quality and quantity30,31
- Elevated sexual interest32 and greater intercourse frequency5
- Enhanced sexual performance32
- Lowered blood cholesterol levels,5 and
- Reduced blood pressure.5,9
This combination may provide additional health benefits via stimulation of nitric oxide production.
Nitric oxide modulates the release of neurotransmitters33 and acts as a neurotransmitter involved in long-term memory.34-37 It promotes a healthy immune function38 and favorably modulates vascular tone, coagulation, and fibrinolysis.39
Clinical Studies of French Maritime Pine-Bark Extract and Arginine

Scientists treated erectile dysfunction patients aged 25 to 45 with L-arginine aspartate.
After a month, only 5% of patients had normal erections. In month two, however, 80 mg of French maritime pine-bark extract was added to the regimen, and by month’s end, a remarkable 80% of men experienced normal erectile function.
In the third month, the pine-bark extract dosage was increased to 120 mg, and at the end of that month, 92.5% of participants achieved normal erectile function.8
In a second clinical trial—a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover design—researchers examined 50 middle-aged men with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction. They treated them with placebo or with French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine aspartate. Participants recorded their degree of sexual function or dysfunction, and investigators monitored testosterone levels and endothelial nitric oxide synthase levels along with clinical chemistry.
These nutrients restored erectile function to normal and doubled intercourse frequency within one month. Nitric oxide synthase in spermatozoa and blood testosterone levels also increased significantly. When looking at the vascular effects of this nutrient combination, blood cholesterol and blood pressure decreased.5
In another double-blind study, patients with mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction were treated with a supplement that delivered either a placebo or a daily dose of 60 mg of French maritime pine-bark extract, 690 mg of L-arginine, and 552 mg of aspartic acid. The results were assessed using the International Index of Erectile Function test. Blood biochemistry, urinalysis, and salivary testosterone were also measured.
After eight weeks, there was marked improvement in the total erectile dysfunction score, including erection hardness, and satisfaction with sexual intercourse. Notably, there was a significant decrease in blood pressure and a slight boost in salivary testosterone—with no adverse reactions.9
A fourth clinical trial was conducted in 2015 on 47 patients with mild erectile dysfunction and abnormally low sperm numbers combined with low sperm motility and a low level of healthy-shaped sperm.
The men received daily doses of 60 mg of French maritime pine-bark extract, 690 mg of L-arginine, and 552 mg of aspartic acid. Four months later, erectile dysfunction was “significantly ameliorated,” and average sperm concentration was notably increased. No unwanted effects were noticed or reported.7
Underscoring these effects, a 2017 study found that a significant proportion of erectile dysfunction patients have low levels of L-arginine. These levels were 17% lower in men with complete erectile dysfunction. The authors concluded that low L-arginine levels may “increase the erectile dysfunction risk by reducing the concentration of nitric oxide,” which is essential to vascular health.6
These and other clinical studies further confirm the ability of French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine aspartate to restore erectile function,5 reverse low male fertility values by improving sperm quality30,31 and semen volume,30 and double intercourse frequency.5
Icariin Sustains Erectile Function

Chinese medicine practitioners claim that icariin—a flavonoid extracted from plants in the Epimedium genus—produces aphrodisiac effects and restores erectile function.
Scientists agree that its multiple mechanisms of action suggest that icariin does support healthy erectile function.
Like Viagra®, Cialis®, and Levitra®, icariin blocks the action of the enzyme that causes erections to subside.29,40-42 Icariin also enhances the production of nitric oxide both in human endothelial cell culture and in animal models.43-45
Scientists have noted that icariin behaves similarly to testosterone—significant because testosterone is crucial for healthy sexual function.46
Research found that Epimedium extracts improve erectile function in aged rats47 and that icariin molecules enhance erectile function in diabetic rats by promoting nitric oxide production.48
These multiple mechanisms suggest that icariin—like French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine—supports normal erectile function.
Beyond Erectile Dysfunction—Improving Sperm Quality
 |
Double-blind, placebo-controlled studies demonstrate that French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine aspartate safely treat erectile dysfunction.5,7-9 But these natural nutrients have also been shown to improve sperm quality and fertility.
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, scientists evaluated the effects of French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine aspartate on spermatozoa parameters in 50 middle-aged men diagnosed with infertility. Sperm quality was markedly improved, with better results in younger men.31
In another double-blind, placebo-controlled study, researchers treated 50 infertile men for one month with either placebo or French maritime pine-bark extract and L-arginine aspartate. Compared with placebo treatment, these two compounds significantly increased:30
- Semen volume,
- Concentration of spermatozoa,
- Percentage of motile spermatozoa, and
- Percentage of spermatozoa with normal morphology.
In one month, this dual-nutrient treatment restored the fertility index to normal values. After treatment was discontinued, the fertility index decreased again to infertile status. No adverse events were reported.30
Summary

Many aging men with erectile dysfunction are deemed to have a “sexual disorder” and subsequently are prescribed costly drugs, such as Cialis®, that provide temporary relief for only about half of patients.
Erectile dysfunction, however, is one of the earliest symptoms of coronary artery disease, occurring up to three years before a heart attack.
Compelling research demonstrates that certain nutrients boost levels of nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels and enables efficient blood flow—critical for both healthy male sexual function and overall vascular health.
In 2017, scientists demonstrated that a significant proportion of erectile dysfunction patients have low levels of L-arginine, which is needed to produce nitric oxide to promote blood flow.
Consistent research findings show that supplementing with arginine compounds, pine-bark extract, and the flavonoid icariin provides safe and rapid improvement not only in erectile dysfunction, but also in underlying cardiovascular cofactors.
If you have any questions on the scientific content of this article, please call a Life Extension® Wellness Specialist at 1-866-864-3027.
References
- Available at: http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9901E5DB163EF93AA1575BC0A96F9C8B63. Accessed May 31, 2017.
- Jackson G. Prevention of cardiovascular disease by the early identification of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20 Suppl 2:S9-14.
- Schoonees A, Visser J, Musekiwa A, et al. Pycnogenol(R) (extract of French maritime pine bark) for the treatment of chronic disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012(4):Cd008294.
- Wu G, Meininger CJ. Nitric oxide and vascular insulin resistance. Biofactors. 2009;35(1):21-7.
- Stanislavov R, Nikolova V, Rohdewald P. Improvement of erectile function with Prelox: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20(2):173-80.
- Barassi A, Corsi Romanelli MM, Pezzilli R, et al. Levels of l-arginine and l-citrulline in patients with erectile dysfunction of different etiology. Andrology. 2017;5(2):256-61.
- Kobori Y, Suzuki K, Iwahata T, et al. Improvement of seminal quality and sexual function of men with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia syndrome following supplementation with L-arginine and Pycnogenol(R). Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015;87(3):190-3.
- Stanislavov R, Nikolova V. Treatment of erectile dysfunction with pycnogenol and L-arginine. J Sex Marital Ther. 2003;29(3):207-13.
- Aoki H, Nagao J, Ueda T, et al. Clinical assessment of a supplement of Pycnogenol(R) and L-arginine in Japanese patients with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction. Phytother Res. 2012;26(2):204-7.
- Banks E, Joshy G, Abhayaratna WP, et al. Erectile dysfunction severity as a risk marker for cardiovascular disease hospitalisation and all-cause mortality: a prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2013;10(1):e1001372.
- Fode M, Krogh-Jespersen S, Brackett NL, et al. Male sexual dysfunction and infertility associated with neurological disorders. Asian J Androl. 2012;14(1):61-8.
- Diaz-Arjonilla M, Schwarcz M, Swerdloff RS, et al. Obesity, low testosterone levels and erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2009;21(2):89-98.
- Gregorian RS, Golden KA, Bahce A, et al. Antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction. Ann Pharmacother. 2002;36(10):1577-89.
- Lane-Cordova AD, Kershaw K, Liu K, et al. Association Between Cardiovascular Health and Endothelial Function With Future Erectile Dysfunction: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Am J Hypertens. 2017.
- Baldwin K, Ginsberg P, Harkaway RC. Under-reporting of erectile dysfunction among men with unrelated urologic conditions. Int J Impot Res. 2003;15(2):87-9.
- Eisenberg ML, Li S, Cullen MR, et al. Increased risk of incident chronic medical conditions in infertile men: analysis of United States claims data. Fertil Steril. 2016;105(3):629-36.
- Nascimento ER, Maia AC, Pereira V, et al. Sexual dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review of prevalence. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013;68(11):1462-8.
- Available at: http://www.cbsnews.com/news/sex-erectile-dysfunction-drugs-viagra-cialis-addyi-medicines-cost/. Accessed June 1, 2017.
- Available at: http://www.rxlist.com/viagra-side-effects-drug-center.htm. Accessed May 31, 2017.
- Lim PH, Moorthy P, Benton KG. The clinical safety of viagra. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;962:378-88.
- Blonde L. Sildenafil citrate for erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors: a retrospective analysis of pooled data from placebo-controlled trials. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22(11):2111-20.
- Laties AM. Vision disorders and phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: a review of the evidence to date. Drug Saf. 2009;32(1):1-18.
- Santaella RM, Fraunfelder FW. Ocular adverse effects associated with systemic medications : recognition and management. Drugs. 2007;67(1):75-93.
- Bella AJ, Brant WO, Lue TF, et al. Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) and phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors. Can J Urol. 2006;13(5):3233-8.
- Mukherjee B, Shivakumar T. A case of sensorineural deafness following ingestion of sildenafil. J Laryngol Otol. 2007;121(4):395-7.
- Choi HK, Ahn TY, Kim JJ, et al. A double-blind, randomised- placebo, controlled, parallel group, multicentre, flexible-dose escalation study to assess the efficacy and safety of sildenafil administered as required to male outpatients with erectile dysfunction in Korea. Int J Impot Res. 2003;15(2):80-6.
- Kruuse C, Thomsen LL, Birk S, et al. Migraine can be induced by sildenafil without changes in middle cerebral artery diameter. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 1):241-7.
- Huang PL. eNOS, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20(6):295-302.
- Ning H, Xin ZC, Lin G, et al. Effects of icariin on phosphodiesterase-5 activity in vitro and cyclic guanosine monophosphate level in cavernous smooth muscle cells. Urology. 2006;68(6):1350-4.
- Stanislavov R, Nikolova V, Rohdewald P. Improvement of seminal parameters with Prelox: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Phytother Res. 2009;23(3):297-302.
- Nikolova V, Stanislavov R, Vatev I, et al. Sperm parameters in male idiopathic infertility after treatment with prelox. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2007;46(5):7-12.
- Available at: http://www.touchendocrinology.com/sites/www.touchendocrinology.com/files/lamm.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2017.
- Prast H, Philippu A. Nitric oxide as modulator of neuronal function. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;64(1):51-68.
- Schuman EM, Madison DV. A requirement for the intercellular messenger nitric oxide in long-term potentiation. Science. 1991;254(5037):1503-6.
- Paul V, Ekambaram P. Involvement of nitric oxide in learning & memory processes. The Indian Journal of Medical Research. 2011;133(5):471-8.
- Jacoby S, Sims RE, Hartell NA. Nitric oxide is required for the induction and heterosynaptic spread of long-term potentiation in rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 2001;535(Pt 3):825-39.
- Hawkins RD, Son H, Arancio O. Nitric oxide as a retrograde messenger during long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Prog Brain Res. 1998;118:155-72.
- Nussler AK, Billiar TR. Inflammation, immunoregulation, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Leukoc Biol. 1993;54(2):171-8.
- Corseaux D, Ollivier V, Fontaine V, et al. Hemostasis imbalance in experimental hypertension. Mol Med. 2002;8(4):169-78.
- Jiang Z, Hu B, Wang J, et al. Effect of icariin on cyclic GMP levels and on the mRNA expression of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) in penile cavernosum. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2006;26(4):460-2.
- Xin ZC, Kim EK, Lin CS, et al. Effects of icariin on cGMP-specific PDE5 and cAMP-specific PDE4 activities. Asian J Androl. 2003;5(1):15-8.
- Dell’Agli M, Galli GV, Dal Cero E, et al. Potent inhibition of human phosphodiesterase-5 by icariin derivatives. J Nat Prod. 2008;71(9):1513-7.
- Xu HB, Huang ZQ. Icariin enhances endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression on human endothelial cells in vitro. Vascul Pharmacol. 2007;47(1):18-24.
- Tian L, Xin ZC, Liu WJ, et al. Effects of icariin on the erectile function and expression of nitrogen oxide synthase isoforms in corpus cavernosum of arterigenic erectile dysfunction rat model. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004;84(11):954-7.
- Liu WJ, Xin ZC, Xin H, et al. Effects of icariin on erectile function and expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in castrated rats. Asian J Androl. 2005;7(4):381-8.
- Zhang ZB, Yang QT. The testosterone mimetic properties of icariin. Asian J Androl. 2006;8(5):601-5.
- Makarova MN, Pozharitskaya ON, Shikov AN, et al. Effect of lipid-based suspension of Epimedium koreanum Nakai extract on sexual behavior in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;114(3):412-6.
- Zhang J, Li AM, Liu BX, et al. Effect of icarisid II on diabetic rats with erectile dysfunction and its potential mechanism via assessment of AGEs, autophagy, mTOR and the NO-cGMP pathway. Asian J Androl. 2013;15(1):143-8.

